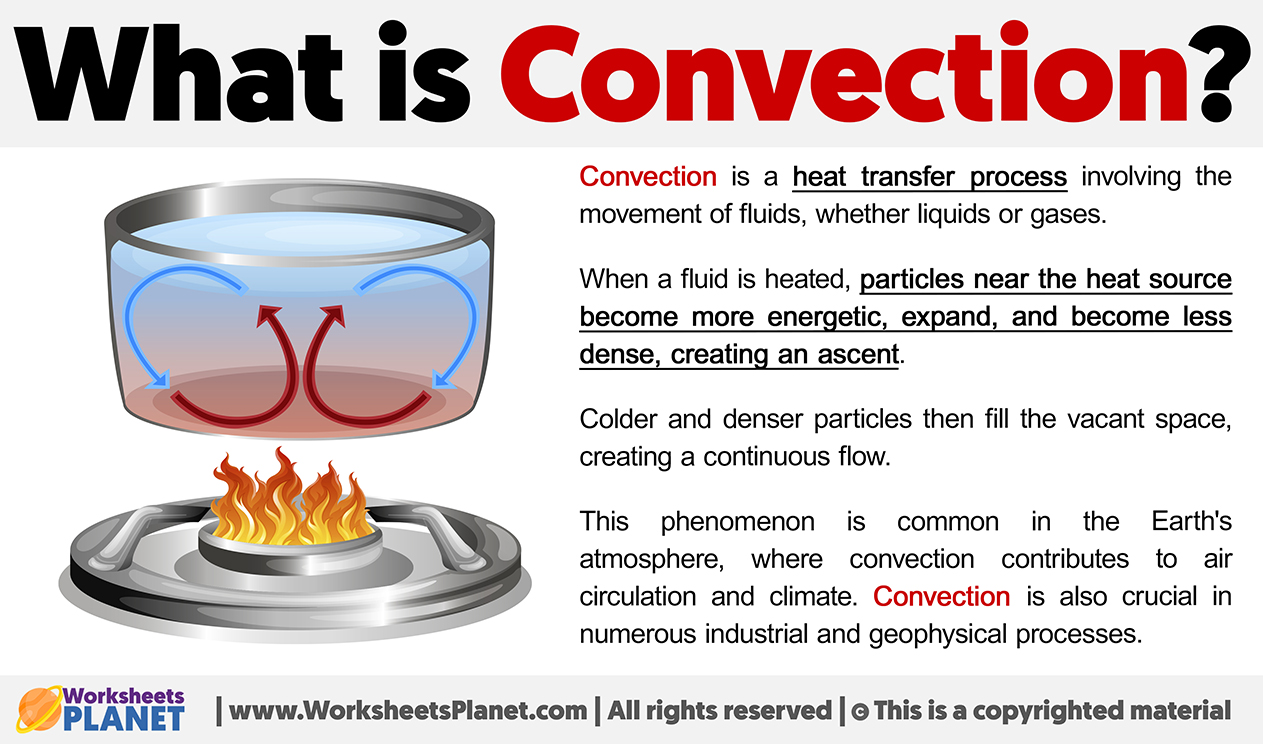
Convection is a heat transfer process involving the movement of fluids, whether liquids or gases. When a fluid is heated, particles near the heat source become more energetic, expand, and become less dense, creating an ascent.
Colder and denser particles then fill the vacant space, creating a continuous flow.
This phenomenon is common in the Earth’s atmosphere, where convection contributes to air circulation and climate. Convection is also crucial in numerous industrial and geophysical processes.